Treat Your Eczema With Homeopathic Medicine
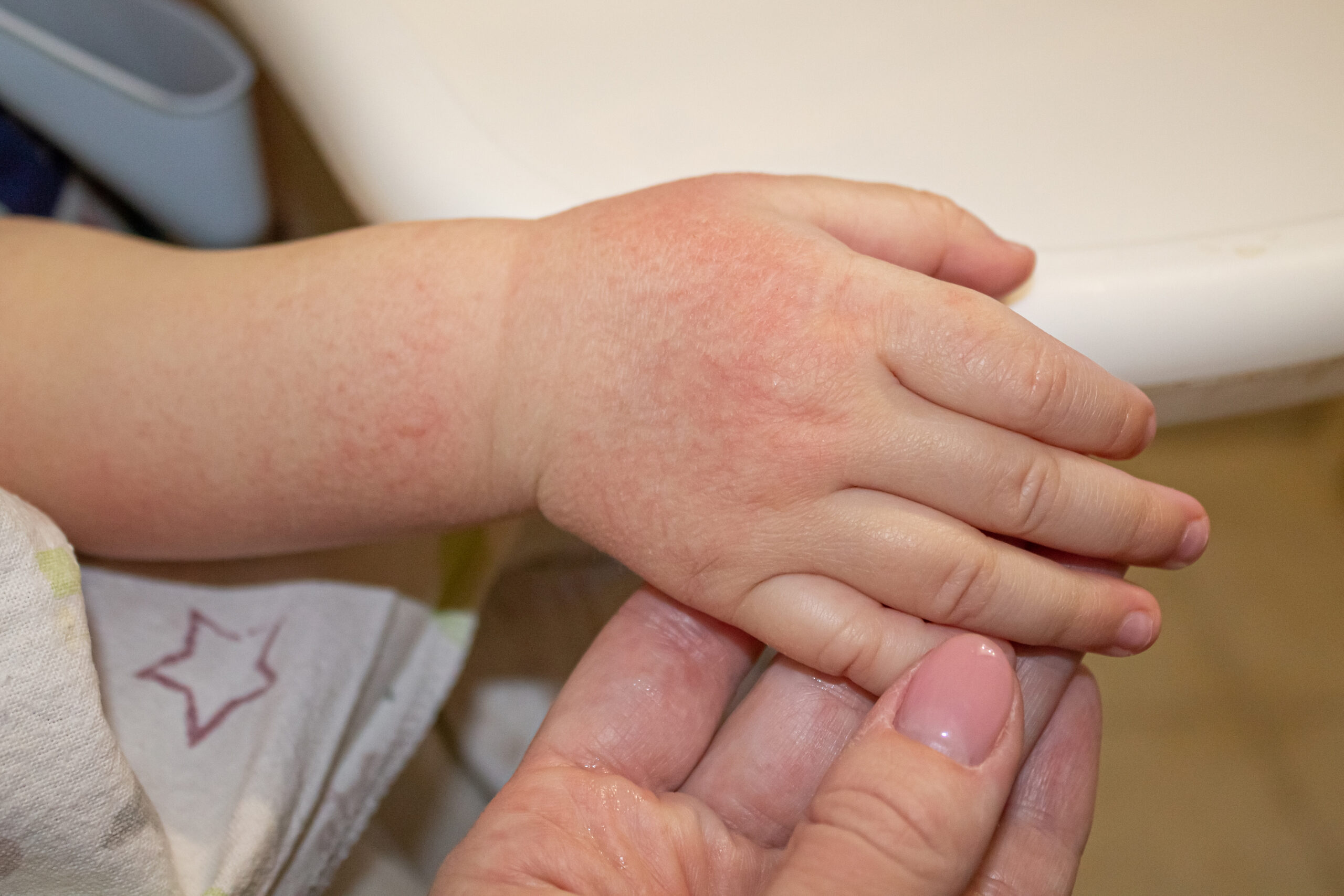
Eczema is a prevalent skin condition that is long-lasting, not contagious and is characterized by dry skin, red scaly patches in one area, intense itchiness, and skin discomfort. This condition can also be referred to as atopic eczema, neurodermatitis, or atopic dermatitis. It affects a proportion of 20% of children and 10% of the adult population in India and ranks as the 15th most common non-fatal disease worldwide and is the leading skin disease in terms of disability-adjusted life years (DALYs).
The skin eruptions linked with eczema are recognizable due to the presence of small raised bumps, the formation of crusts and scales, and fluid-filled blisters on reddened and swollen skin. Though, in darker skin, it might be tough to recognize the redness. When the eruptions or scales persist for long periods, the skin might thicken resulting in a condition called lichenification.
The causes of eczema are linked to a genetic variation that affects the skin’s capacity to offer protection. Due to a weakened barrier function, the skin becomes less capable of retaining moisture and safeguarding against bacteria, irritants, allergens, and environmental factors such as tobacco smoke. Other causes include the excessive presence of Staphylococcus aureus bacteria on the skin.
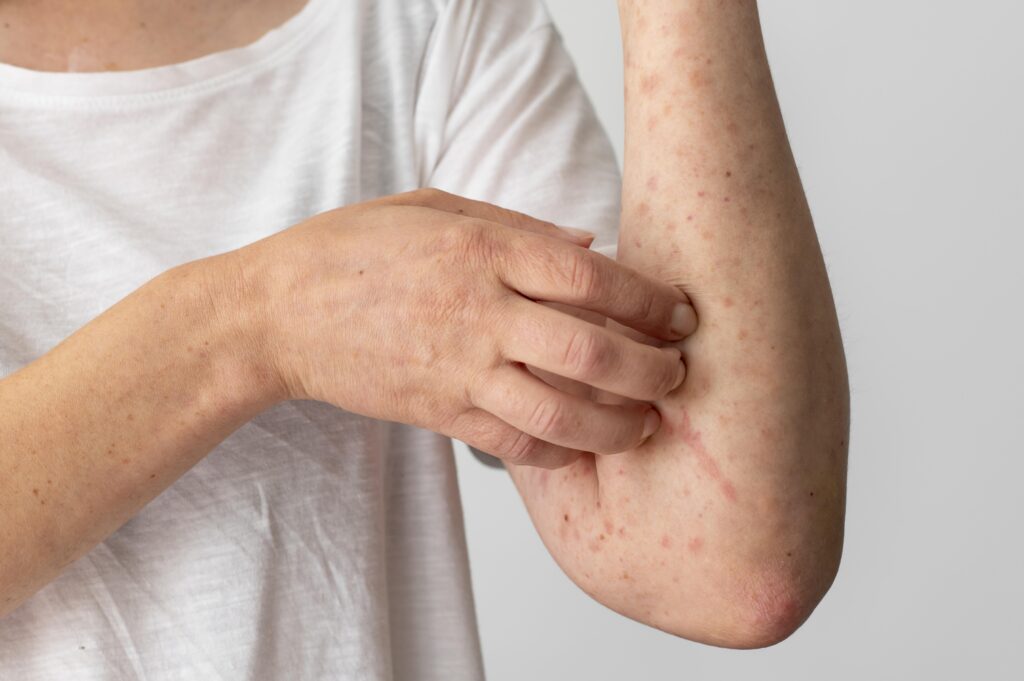
Types of Eczema
| S.no | Types | Indications |
| 1. | Atopic Dermatitis – | This type of eczema leads to dryness, inflammation, and itching in the affected area. It usually affects young children and can happen to people of any age. |
| 2. | Contact Dermatitis – | Also known as allergic contact dermatitis, is caused by environmental factors. |
| 3. | Neurodermatitis or – Discoid Eczema | This form affects small patches of skin. It makes them itchy and scaly. |
| 4. | Dyshidrotic Eczema – | The skin can become dry and a person may experience a burning sensation, rashes and blisters with this form of eczema. |
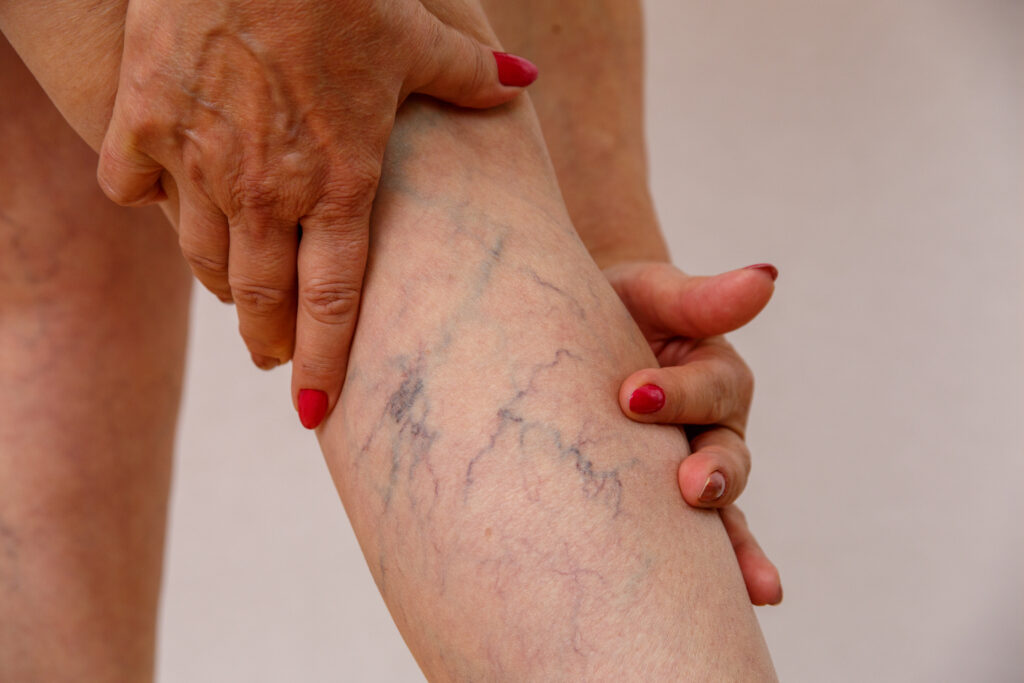
| 5. | Nummular Eczema – | This condition results in the development of circular lesions throughout the entire body, with a particular prominence on the arms and legs. |
| 6. | Seborrheic Dermatitis – | A type of eczema that causes inflammation specifically on the scalp. |
| 7. | Stasis Dermatitis – | A condition characterized by changes in skin coloration on the legs that resemble varicose veins. |
The American Academy of Dermatology states that the clinical diagnosis of eczema is determined by examining skin signs, identifying the location of the skin lesions, noting any related clinical findings, and determining if there is a history of atopy in the individual or their family. It is crucial to seek advice from a dermatologist, as each variant of this disease has its characteristic triggers and treatment requirements.
Treatment of eczema usually involves oral antibiotics, corticosteroids, and topical medications such as creams, gels, or ointments, which are applied directly to the affected skin to alleviate itching and reduce redness and swelling. It can be managed with lukewarm baths using a mild soap and applying moisturizer every day on the skin and by wearing cotton or soft fabrics clothes.
Homeopathic Management Of Eczema
Homeopathy is a holistic system of treatment that is safe, effective and involves the use of highly diluted substances to treat a variety of skin conditions, including eczema.
Homeopathic remedies for eczema are based on the principle of “like cures like,” meaning that a substance that causes similar symptoms in a healthy person is used to treat those symptoms in a sick person.
Homeopathy can help the body to move towards a healthier state and improve eczema by balancing the immune system. The chances of improvement are high because the body is capable of regulating itself.
The healing process follows Hering’s law of cure, where the deepest level symptoms are the first to improve, followed by the less severe ones.
If treatment is successful, the overall health of an individual will improve before eczema improves, starting with the face and trunk, and lastly, the extremities. According to the Homeopathic concept of disease, eczema is linked to the Psoric miasm, typically seen in individuals who have a sensitive, weak, and reactive personalities. They often have a tendency to develop chronic skin problems, which can be aggravated by stress, anxiety, and emotional imbalances.
In Previous studies, it was found that Graphites 30C shows good improvement in all symptoms of this problem. In another study most frequently prescribed homeopathic medicines were Calcarea carbonicum, Tuberculinum, and Medorrhinum.
Homeopathic Therapeutics
- Sulphur: Used when the skin is dry, scaly, and itchy, with a burning sensation.
- Graphites: Useful for treating dry, cracked, and scaly skin.
- Arsenicum album: It is recommended for itchy, burning, and painful eczema that is aggravated at night.
- Petroleum: Helps to relieve eczema with cracks that bleed, especially on the hands, fingers, and feet.
- Natrum muriaticum: It is used for eczema that is triggered by emotional stress and has a tendency to form blisters.
Conclusion
Homeopathy aims to stimulate the body’s natural healing process and improve the patient’s overall health and can provide a long-term solution to eczema, promoting overall well-being and improving patients’ quality of life. To accurately determine the effectiveness of homeopathic treatment for eczema, it is necessary to conduct larger studies using various study designs and larger groups of participants.



can we take only sulphur in 30 p.for curing eczema?
I stumbled upon this article and it’s truly a gem I admire its ability to deliver valuable insights with utmost clarity and brevity.